Commercial Rabbit farming in Nigeria is one of the agricultural business our youths can venture into. Millions of tons of this meat are consumed yearly either for meat production, fur production, pharmaceutical uses or even as a pet.
Commercial rabbit farming system is targeted at the production of rabbits in large quantities, which are marketed for different purposes as mentioned earlier. Even the urine and droplets of rabbits have their way of generating income for the farmer. However, starting a rabbit farm does not require much capital and time as there are a series of common breeds to be specialized in as a beginner in the business.
For these reasons, the last edition of Afrimash online training that held between the 29th and 30th of April, 2020 was to build capacity for farmers to venture into this profitable agribusiness. But before we go into the details of Rabbit Farming, it is important to introduce the facilitator of the training.
Facilitator: Mr Faleke John
Mr Faleke John is the CEO of Faleks Farm. He is also a vendor on Afrimash. He has experience in snail farming, rabbit farming and pig farming.

He took us on how to make a profit from rabbit rearing through this outline;
- Rabbit Breeds and Breeding Stock
- Rabbit Feeds and Feeding
- Rabbit Housing Facilities
- Rabbit Diseases and Treatment
- Marketing Your Rabbit
- Processing and Packaging Rabbit Meat
Rabbit Breeds and Breeding Stock
Breeds
Some common breeds of rabbit in Nigeria at the moments include the following;
- New Zealand: They are friendly and grow to 5kg at maturity. They are a good source of meat and fur production.
- Flemish Giants: They grow up to 7kg at maturity and they are also good for meat production and their coat is also a good source of income for the farmer.
- English Spot: They are medium size rabbits and grow up to 3kg very friendly and their fur can also be a source of income
- Chinchillas: They grow to 3.5-4kg if well fed and can be a good source of meat, pet and fur productions.
Other brands include British Giants, Dutch Rabbits, English Angora, California, Dwarf Lop, English Lop, Hylas etc.
Breeding Stock
A female mature rabbit can be used to breed other rabbits by just placing her with a mature Buck of a different breed. New Zealand male crossed with a female Chinchilla will produce Chinchilla and New Zealand weaners. The same applies to other breeds.
The Doe, which is the female rabbit, should not be left with the Buck for more than three days before separation. The separation date should be noted to be able to calculate the due date for the doe which is usually between 28-31 days
A male rabbit can be used to cross another female rabbit in every four days after being separated from other females. A female old rabbit can be replaced with a younger one for production between 3-5 years when her production becomes low.
The gestation period of a female rabbit is between 28-31 days and can produce between (6-12 babies at a time) and 4-5 times yearly.
Rabbit Feeds and Feeding

We have different types of grasses in Nigerian that rabbits can be fed on. They can feed on yam and cocoyam peels, weeds, banana, pineapple corns, vines from pulses, leaves, carrots, cabbage, lettuce, and lots more.
The best feed for rapid growth is pellet, made from certain animal feeding formula.
It is recommended that rabbits should be fed twice daily just like the normal way and system of feeding our broilers and Cockerels at home.
Apart from weaners or when crossing, rabbits should live alone in separate rooms in their cages with a feeder and a drinker, either concrete or metal.
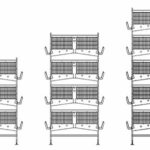
Rabbit Housing Facilities
A good housing facility with an adequate arrangement of ventilation is the most important factor in rabbit house. Good house denotes proper cages or hutches and arrangement for feeding, watering, and cleaning. House is important to keep the rabbit in one roof and to prevent them from running away.

There are several ways of housing rabbits. This depends on financial involvement and the climate of the place. In backyard rabbit farming, locally available materials are used. The commonly used materials include tin cans, bamboos, old boxes, wood, bricks, asbestos sheets etc. Katcha floor and walls may be the components of the house.
Cages can be constructed by the farmer, or a professional can be consulted. The cages can be constructed at your backyard, but the living area of the rabbit must not be too cold or hot so as not to damage their health.
Rabbits require adequate water supply even though they consume less water when they feed on grasses alone
Caution: Always study the drops of your rabbit when introducing new feeds, the drops should not be watery so you should give them new feeds in small quantities and study them until they master them.
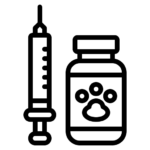
Rabbit Diseases and Treatment
- Coccidiosis: This can injure the bile ducts, intestines or cecum. It affects primarily young rabbits. In severe cases, symptoms are diarrhoea, loss of flesh, pot belly, loss of appetite, rough fur coat. It can be prevented by keeping pens clean and also avoid faecal contamination of feed and water. Use wire floor pens.
Treatment: Add Sulfaquinoxaline in food or drinking water continuously for 2 weeks.
- Ear Canker: Ear mite scabs or a crust start forming at the base of the inner ear. Mites cause considerable irritation, and the rabbit will shake its head and try to scratch ears with hind feet. Do not let unaffected rabbits in contact with rabbits that have ear canker.
Treatment: Use a cotton swab to apply mineral, vegetable or olive oil over all visible crust. Usually, one or two treatments is sufficient.
- Eye Infection: This is caused by several types of bacteria. The eyes of baby rabbits may stick shut and pus around the eyes may be noticed. Prevent cold drafts and other stress conditions.
Treatment: Apply an antibacterial ophthalmic eye ointment.

- Fur Block “Hair Ball”: Rabbit ingests a large amount of its hair or that from another rabbit in a short time. They will sporadically eat small amounts of feed. A firm mass can be palpated in the stomach.
Treatment: An oral dose of 1/2 oz. mineral oil may be effective. If the fur block is too large, surgical removal is necessary.
- Fungus Infection: A dry scaly skin (dandruff) on the shoulders and back. Prevent contact with affected rabbits.
Treatment: Apply Tolnaftate to the affected area.
- Heat Exhaustion: Excessively high temperatures (above 85oF) and high humidity (above 70%), obesity, poor ventilation, insufficient water and crowding. Increased respiration rate (panting), prostration, and excessive saliva discharge. Pregnant Does and young in the nest box are most susceptible. Provide shade, adequate air movement, and plenty of cool water on a hot day. Wet burlap in the cage will aid in cooling.
Treatment: Rabbits suffering from heat exhaustion can be immersed in lukewarm water to reduce body temperature to the normal 101-104oF. Apply a cool compress to the ears.
- Ketosis: Obesity, large litter, lack of exercise. It usually occurs just before or immediately after kindling. Does go off feed and will not eat. Prevent young Does from getting too fat and make sure they are eating at kindling time.
Treatment: Obesity can be prevented by limiting feed to 4 to 6 oz. daily for does.
- Mastitis “Blue Breast”: A bacterial infection in the mammary gland caused by an injury from the nest box, cage or a bite from nursing young. The mammary gland will become red, swollen, tender and dark blue streaks may appear. Reduce any chance of injury to mammary gland as the doe enters the nest box. Do not transfer the young to another lactating Doe.
Treatment: Penicillin is effective against staphylococcus or streptococcus organisms.
- Malocclusion “Buck teeth”: An inherited condition characterized by excessive growth of the front teeth. Lower teeth protrude and upper teeth curve into the mouth. Do not use rabbits with “buck teeth” for breeding purposes.
Treatment: Teeth on young rabbits can be trimmed until they reach slaughter weight.
Marketing Your Rabbit:
To sell your rabbits profitably and steadily, you need to create your marketing channels.
Selling channels include the following:
- Online e-adverts or marketing
- Processed rabbit meat can be supplied to supermarkets for people to buy.
- Local markets display them in the local market like live chicken, turkeys and the likes
- Pharmaceutical companies use rabbit for experiments
- Restaurant and food sellers. Most people demand it because it has varieties of health benefits as a white meat
- Individuals also demand rabbits and rear as pets, and farmers also make the demand to start up a new rabbit farm.
- Rabbits’ drops are another source of income to the breeder. We supply them to crop farmers in bags for manure. Also, farmers can reduce the money they spend on pesticides by using rabbit urine to wipe insects that attack crops.
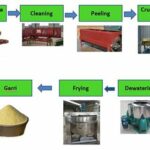
Processing and Packaging Rabbit Meat
- After slaughtering the animal, skin the fur and remove the intestine.
- Washing the carcass thoroughly, hang it to drain.
- Wipe excess water with a clean cloth, and pack meat attractively in a cellophane bag.
- Record weight on the bag and refrigerate.
You can check YouTube for live video on how to slaughter and skin the rabbit

In conclusion, medications and vaccinations play a vital role in ‘Rabbitry’. We recommend that the rabbit should be given antibiotics and multivitamin monthly mixed into their water. While the antibiotics prevent diseases, the multivitamin helps them to feed well and look healthy.
Finally, we suggest a new farmer should start up a Commercial Rabbit Farming with three colonies of the desired breed. If you have three colonies of rabbits comprising twelve females and three males, then you should not expect your stock to be less than (400) within a year. If well taken care of and well managed.
Questions
Question: What is the prospect of commercial rabbit farming in Nigeria? Which of the breed is good for meat production in a sustainable manner?
Response: Rabbit meat has a lot of nutritional value and has no side effect on the body system. It builds up the body system, especially for aged people. So with the unrelenting awareness, a lot of people will prefer rabbit meat to other meat which means the demand will become higher. New Zealand, Chinchillas, Hylas, Flemish Giant are all good for meat production, they grow faster and mature in 16 weeks if well-fed with a proper food ration.
Question: Where can I source for Hylas and Flemish Giant? I noticed it’s only New Zealand White and Chinchillas that are available on Afrimash.
Response: New Zealand and Chinchilla is my area of concentration because they grow faster bigger and produce easily more. By produce more I mean they get pregnant easily and produce more kitten. Up to 12 at a time.
Question: What is the best feed for kits with mother and how will the feeding be as weaner.
Response: The best feed for rabbit kits is their mother’s milk while their mother is fed on pellets and grasses, which must be provided with adequate water. The kits will start feeding on pellets and grasses 21 days after birth.
Question: How can a rabbit farmer reduce mortality of weaners?
Response: Make sure the cage is well cleaned daily to prevent all kinds of bacteria, fungi and other diseases. Provide adequate feed, water and adequate space for them to run and play around within the cage.
Question: What brand of anti-coccidiosis will you recommend and mode of application with dose?
Response: For anti-coccidiosis dosage and application, please visit any animal clinic close to you. Dry grasses are the best. I mean fresh grass without water. When serving your rabbit wash grass thoroughly and let it dry before serving your rabbit.
Question: Do you have high pedigree New Zealand White for sale?
Response: All our breed as advertised on Afrimash are pure breeds.
Question: Many rabbit farmers are saying it is rare to have a quality breed of NZW in Nigeria. When it is the appropriate time to wean rabbit kits and rebreed the mother?
Response: Between 4-6 weeks.
Question: What can you do when Does are not ready to be breed by Buck? I have at least 3 on my farm for about a month now. Any remedy or something to do?
Response: You are right some female doe is difficult to mate. The option is to hold the female for the male to mate. If you invite us to your farm, I will teach you how to do it.
Question: But many farmers called it forced breeding and they say it may not be as successful as natural. I will be looking out for your experience on this.
Response: That’s why I will call it an option B. We have tried it and it’s working perfectly.
Question: Is mentoring allowed at the end of this contact. Between the lecturer and students?
Response: This is encouraged that is why the training was created, so you have this advantage over others who didn’t pay.